Technology
fundingA profitable business. Enthusiasts pay hundreds of thousands of dollars for Ukrainian gadgets

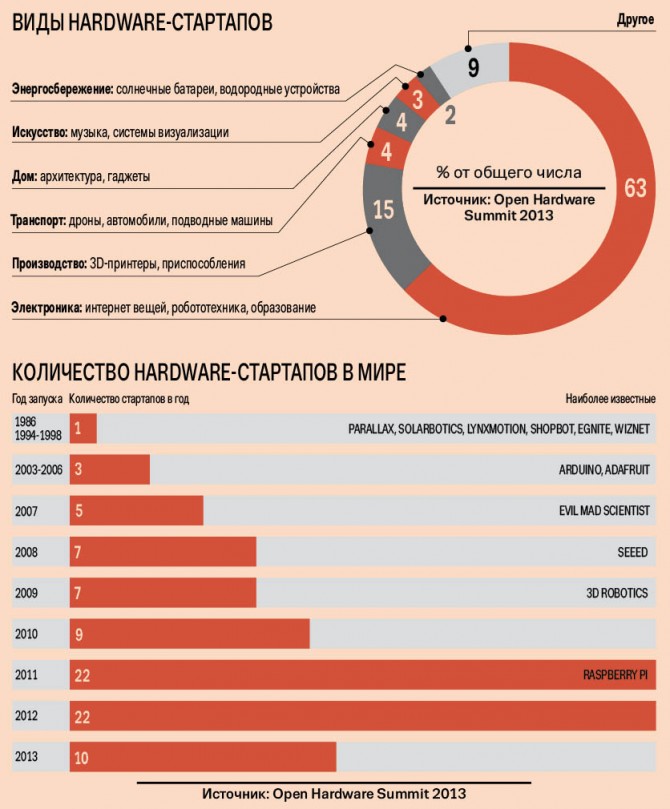
The startup «ecosystem» began forming in Ukraine only several years ago, but has already faced a serious challenge. Along with projects aimed at the development of software, the first gadgets (hardware) developed by first-time entrepreneurs from Ukraine appeared.
There are not many such hardware startups at the moment – from 5 to 10, tells Nazar Bilous, founder of the Smart Atoms company. Yesterday his company introduced to the broad public its newest development: a smart desktop gadget called LaMetric, which features a clock, weather reports, Paypal live balances and transactions, a Facebook fan counter and notifications from other internet services. The project raised funds through Kickstarter, a crowd-funding platform. According to information on the Kickstarter’s website, LaMetric is planning to raise at least USD 69,000. An hour after the launch of the campaign (as the issue was being sent to print), it managed to collect USD 14,500 in donations.
From the Internet to the plant
Kickstarter is so far the best option to raise money for production of the first shipment of the gadget, says Ivan Pasechnyk, CEO of the EcoisMe project and co-founder of the techno-geek community HackLab, particularly since there are already companies in Ukraine that provide professional assistance for launching the projects of startups on Kickstarter. For instance, the ARTKB design bureau last year helped organize the campaign and production for Petcube (a gadget that plays with your pets and helps you communicate with them, when you are not at home) and iBlazr (a LED flash for iPhone). The former raised USD 251,000 on Kickstarter and the latter – USD 150,000.
Before the start of the campaign, a prototype is usually produced. “This is before the funds are raised and the contractor is chosen that will organize serial production,” shares Pasechnyk. The process of launching serial production is very complex and often takes as much time as the development of a gadget, explains co-founder of ARTKB Oleksandr Nesterenko. Based on the strategy of business development, the decisions are made on the country of serial production and the logistics. Then follow the calculation of the economy of production, selection of suppliers and contractors, setting the technical task, formulation of quality requirements, coordination of production processes, technologies, instrument and quality control, logistics and certification. There is a very long path from a document to serial production and it is largely unique for each particular product.
Fears of investors
CEO of Detonate Ventures Natalia Berezovska is one of the backers (donors) at Kickstarter. She donates money to different projects as a private individual. However, as a systemic investor of such projects she is held back by the same problems that exist in any business involved in physical goods. They are production, logistics and shelves – something that makes scaling of such projects not as simple, particularly when the Ukrainian team immediately targets the global market. “I would like to see how the guys succeed in this and only then will I change my attitude towards hardware projects as being investment attractive,” she explains.
Petcube and iBlazr proved that there will be a demand for their products even after they exceeded their financing targets at Kickstarter, adds venture partner of TA Venture Ihor Semenov. This is a good sign for investors. However, there are still many risks, including the probability of production of the copy of the gadget before the original product comes out and complexity of reorientation of the product in case of failure. Design and quality software developed for the specific gadget are also important success factors.
Due to additional risks, TA Venture does not focus on hardware startups, notes Semenov. Initial investments into hardware startups are usually 2-3 times higher than into software startups, says Bilous. CEO of Klatz (developer of smart watch) Dmytro Honcharenko says that at an early stage, investments range from USD 20,000 to USD 100,000 and more.
Favorable environment
Until recently, there has been no «ecosystem» whatsoever for the emergence of hardware projects in Ukraine, says Pasechnyk. Now, there is a community: HackLab (Kyiv), KhackerSpace (Kharkiv), Odessa Hub (Odesa) and Beta Place (Lviv). Hardware accelerator Carrot has been developed on the basis of ARTKB. There was one more place in Donetsk, but it has been seized and mined by separatists, he adds.
As incubators, laboratories and meeting places for “geeks” appear, this environment will be developing, says Nesterenko. “We have such places, but there are very few of them. But we have only just begun and we are developing quite rapidly,” he says.
Bilous believes that people primarily need to overcome their laziness and not be afraid to try and invest their own money. “A person has two-three chances to try and become a businessman over the entire life,” he assures.
As for investors, they also need not fear to try new fields, adds the expert. “The country should not prevent such startups from developing an ecosystem and infrastructure,” he says.
Honcharenko believes that the psychological climate also has an impact on development of the “ecosystem” and hardware communities. “An entrepreneur must be protected against the split-ups, chaos and other ‘charms’ of the transition period. But this applies to any business,” he notes. Personnel is another important and mandatory factor. “Every project requires at least one hardware engineer and, often, an embedded programmer,” emphasizes Honcharenko.
Era of “funny” gadgets
Nesterenko divides all global hardware projects into two categories: “useful or fan things” and “breakthrough technologies”. In order to implement the former, you only need to have a good imagination, business acumen and a good engineer on the team (a mechanic, a hardware engineer, a programmer, etc.), says Nesterenko. Things are different with “breakthrough technology” projects. Usually such projects emerge inside universities, laboratories and similar organizations of the scientific “ecosystem”. Their development requires fundamental research, expensive experiments and a floor for exchanging opinions among the world’s leading scientists. “While the situation is rather positive with the former and there are plenty of professionals, the situation with the latter is rather grim as a couple of good specialists are not enough – the whole scientific sphere needs to be improved,” he explains. For this reason, startups of simple, useful, convenient and funny gadgets are developing most actively in Ukraine.
HARDWARE VS SOFTWARE
How much initial investment into hardware startups differ from investment into software startups?
 Oleksandr Nesterenko, founder of the ARTKB design bureau
Oleksandr Nesterenko, founder of the ARTKB design bureau
It seems to me that it is easier for our guys to bring to the market a hardware project than a software project. You see, people have a lot in common regardless of the country they live in and the language they speak – physiology and basic needs. If it is comfortable for a Chinese to ride a new bike, then it is just as comfortable for an American to ride one. It is easier to hit the target and understand which project will be popular in any part of the world. At the same time, software is all about psychology, mentality and lifestyle. Such things are harder to understand; it is harder to relay them.
 Ivan Pasechnyk, CEO of the EcoisMe project and co-founder of HackLab
Ivan Pasechnyk, CEO of the EcoisMe project and co-founder of HackLab
It is difficult to compare initial investments into hardware startups with software startups. Hardware projects are scaled in line. Though the project may be very successful due to innovations, it starts taking on the form of a bona fide business only after the development of a business model. You cannot have 1,000% growth in a very short period of time, because it will simply be impossible to cope with production.
 Ihor Semenov, venture partner at TA Venture
Ihor Semenov, venture partner at TA Venture
Everything depends on the market they are targeting, on expenses per unit and the margin. In the majority of cases, hardware projects require more investments for development compared to Internet projects.







 of the agreement of syndication with Financial Times Limited are strictly prohibited. Use of materials which refers to France-Presse, Reuters, Interfax-Ukraine, Ukrainian News, UNIAN agencies is strictly prohibited. Materials marked
of the agreement of syndication with Financial Times Limited are strictly prohibited. Use of materials which refers to France-Presse, Reuters, Interfax-Ukraine, Ukrainian News, UNIAN agencies is strictly prohibited. Materials marked  are published as advertisements.
are published as advertisements.